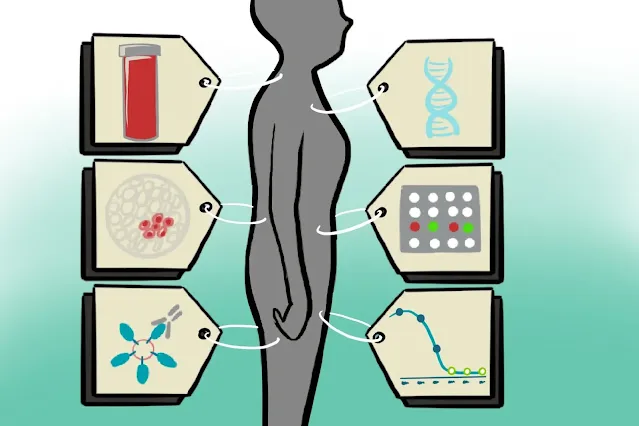
Imagine a world where doctors can predict disease risk, tailor treatments, and monitor progress with a simple test. This isn't science fiction – it's the power of biomarkers. These biological indicators offer a glimpse into our health, and understanding the biomarker landscape is crucial for advancing healthcare.
What are Biomarkers?
Biomarkers are measurable indicators of biological processes, from normal functions to disease development. They can be anything from molecules in our blood to genetic variations, and they hold valuable information about our health. Biomarkers can be used for:
- Early Disease Detection: Identifying individuals at risk for developing diseases like cancer or Alzheimer's before symptoms appear.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments to a patient's specific biology, leading to more effective and targeted therapies.
- Treatment Monitoring: Tracking how well a treatment is working and adjusting it if needed.
The Biomarker Landscape: A Complex Terrain
The landscape of biomarkers is vast and ever-evolving. New discoveries are constantly being made, with researchers exploring different types of biomarkers:
- Genetic Biomarkers: Variations in our DNA that can influence disease risk.
- Protein Biomarkers: Specific proteins whose presence or absence can indicate disease.
- Imaging Biomarkers: Techniques like MRI scans that reveal changes in organ structure or function.
Understanding this landscape requires expertise in various fields, from biology and genetics to medicine and engineering.
The Benefits of Exploring the Biomarker Landscape
The potential benefits of a well-mapped biomarker landscape are significant:
- Improved Diagnosis and Treatment: Biomarkers can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, allowing for timely intervention and improved treatment outcomes.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Early detection and targeted therapies can potentially reduce the overall cost of healthcare.
- Personalized Healthcare Revolution: Biomarkers pave the way for personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to each individual's unique biology.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite the promise, exploring the biomarker landscape isn't without challenges:
- Biomarker Validation: Ensuring a biomarker is truly indicative of a specific disease state.
- Data Sharing and Collaboration: Researchers need to share data efficiently to accelerate progress.
- Ethical Considerations: Ensuring patient privacy and informed consent when using biomarkers.
The Future of Biomarkers
As research continues, the biomarker landscape will become increasingly detailed, revealing new insights into our health. This will lead to advancements in:
- Liquid Biopsies: Non-invasive tests for early cancer detection using biomarkers in blood.
- Companion Diagnostics: Tests that identify patients most likely to benefit from a specific treatment based on their biomarkers.
- Pharmacogenomics: Understanding how individual genetics influence drug response, leading to personalized drug prescriptions.
The exploration of the biomarker landscape holds immense potential for revolutionizing healthcare. As we continue to unveil its secrets, we pave the way for a future of personalized medicine, earlier diagnoses, and more effective treatments for everyone.
Exploring Specific Biomarker Applications
The vastness of the biomarker landscape can feel overwhelming. Let's delve into some specific applications that showcase the power of biomarkers in action:
- Cancer Detection: Biomarkers like blood tests can detect elevated levels of certain proteins associated with specific cancers. Early detection allows for minimally invasive treatment options and significantly improves patient outcomes.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Biomarkers like cholesterol levels and inflammatory markers can predict an individual's risk for heart disease. Early intervention with lifestyle changes or medication can prevent a heart attack or stroke.
- Diabetes Management: Blood sugar monitoring remains crucial, but new biomarkers can offer a more comprehensive picture. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) reflects average blood sugar levels over time, aiding in treatment adjustments.
- Mental Health: The biomarker landscape in mental health is rapidly evolving. Researchers are exploring the potential of identifying biomarkers for depression, anxiety, and even schizophrenia, leading to better diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Beyond Disease: Biomarkers hold potential beyond traditional disease detection. Imagine:
- Personalized Nutrition: Biomarkers could identify your body's optimal nutrient needs, allowing for a personalized diet plan for peak health.
- Fitness Tracking: Biomarkers could track your body's response to exercise, allowing for personalized workout plans that maximize results and minimize injury risk.
- Wellness Monitoring: Biomarkers could track overall health status, including stress levels and sleep quality, empowering individuals to make proactive lifestyle changes for optimal well-being.
The Future is Personalized:
The biomarker landscape is rapidly transforming healthcare from a one-size-fits-all approach to personalized medicine. By identifying individual biomarkers, doctors can tailor treatment plans, predict disease risk, and empower patients to take control of their health.
**The road ahead is exciting, with continuous advancements in biomarker research promising a future of: **
- More Accurate Diagnoses: Biomarkers will lead to earlier and more precise diagnoses, allowing for more effective interventions.
- Targeted Therapies: Treatments will be tailored to an individual's specific biology, leading to improved outcomes and reduced side effects.
- Preventive Healthcare: Biomarkers will identify individuals at higher risk for certain diseases, allowing for preventive measures to be taken.
The exploration of the biomarker landscape is an ongoing journey. As scientists and researchers unlock its secrets, we move closer to a future of personalized medicine, empowered patients, and a healthier world.



.jpg)